Steel sheet and steel plate are two of the most common steel products used throughout a variety of different industries. Often these two products are grouped together, but there are several differences that distinguish them between one another. The main difference deals with the thickness (or gauge) of the material at hand. Steel sheet is categorized as any material that is under 0.187" thick, and steel plate is categorized as any material that has a thickness greater than 0.187".
- Thickness
- Application
- Production Process
The Difference Between Sheet and Plate
The primary difference between steel sheet and steel plate lies in their thickness and the specific applications they are designed for. Steel sheets are thinner, typically ranging from 0.5 mm to less than 6 mm in thickness, and are used in applications that require a lighter, more flexible material. Conversely, steel plates are significantly thicker, generally starting at 6 mm and can go up to several inches, making them suitable for applications that demand high strength and durability.
Additionally, the production processes and uses of steel sheets and plates differ due to their thickness. Steel sheets are often cold rolled for a smooth finish and higher strength, making them ideal for automotive panels, appliance housings, and roofing. On the other hand, steel plates are usually hot rolled and sometimes further treated to enhance their mechanical properties, which makes them suitable for heavy-duty uses such as in construction for structural elements, in the manufacturing of large machinery, and in the production of ship hulls and storage tanks. The distinct thickness and processing methods result in different mechanical properties, which tailor these steel products to their respective applications.
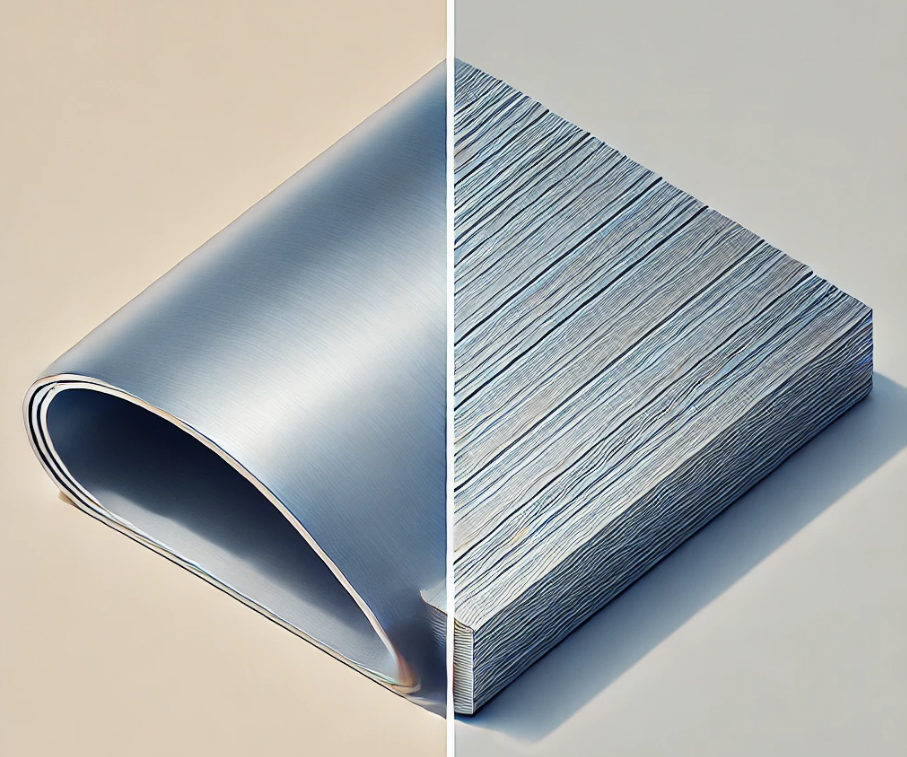
Here is the comparison of a steel sheet and a steel plate. The steel sheet is thinner and smoother, while the steel plate is thicker and more rigid.
Steel Sheet
A steel sheet is a thin, flat piece of steel that is typically produced by rolling the metal into specific dimensions. It is known for its strength, durability, and versatility, making it a popular material in various industries. Steel sheets can be produced in different grades and thicknesses, depending on their intended application. The most common methods of manufacturing steel sheets include hot rolling and cold rolling. Hot rolled steel sheets are created by heating steel above its recrystallization temperature and then rolling it to the desired thickness. Cold rolled steel sheets, on the other hand, are processed at room temperature, which provides a smoother finish and higher strength compared to hot rolled sheets.
Steel sheet is a very versatile product. Some important characteristics include being malleable, thin, lightweight, and having a high tensile strength. This combination of characteristics makes steel sheet a suitable material for a variety of different applications.
Steel sheet is often used in industrial applications such as the construction of buildings or other structures. Some more common applications include home appliances and other interior design purposes. Overall, the wide range of applications for steel sheet are included in industries such as construction, military, oil and gas, mining, and aerospace.
Steel sheets are utilized in a wide range of applications due to their adaptable nature. In the construction industry, they are commonly used for building structures, roofing, and cladding. Automotive manufacturers employ steel sheets in the production of car bodies and parts, owing to their strength and formability. Additionally, steel sheets are essential in the manufacturing of appliances, machinery, and various consumer goods. They can be coated or treated to enhance corrosion resistance, increase durability, or provide specific aesthetic qualities. Overall, steel sheets are an indispensable material that supports numerous sectors with their robust properties and diverse uses.
Steel Plate
Steel plate is any material with a thickness that is greater than 0.187". It is also used across a variety of industries including construction, mining, energy, and manufacturing.
Steel plate is a robust, flat sheet of steel that is significantly thicker than steel sheet, generally exceeding 6 mm in thickness. It is manufactured through a process called rolling, where steel is passed through rollers to achieve the desired thickness. Steel plates are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to heavy loads, making them suitable for demanding applications. They can be produced in various grades and sizes, tailored to meet specific requirements in terms of hardness, toughness, and weldability. The most common methods of manufacturing steel plates include hot rolling, which involves rolling the steel at high temperatures, and quenching and tempering, which enhance the mechanical properties of the steel.
Often steel plate is used in situations where a large amount of fabrication or weldment are required. There are two main types of steel plate, and the distinction comes from the production process. Plate Mill Plates (PMP) are made from ingots and are rolled one plate at a time, whereas Continuous Mill Plates (CMP) are made from a cast slab and rolled as a coiled product.
Steel plates are essential in numerous industries due to their structural integrity and versatile properties. In the construction sector, they are used for building large structures like bridges, skyscrapers, and ship hulls, where their ability to withstand heavy stress is crucial. The oil and gas industry relies on steel plates for constructing storage tanks and pipelines that can endure harsh environmental conditions. Additionally, steel plates are integral in the production of heavy machinery, military equipment, and pressure vessels. They can also be further processed through cutting, welding, and forming to create customized components for specific applications. The durability and strength of steel plates make them a fundamental material in projects that demand high-performance standards.
There are two measurable differences for these products. PMP has widths of 84", 96", and 120", with a thickness ranging between 0.1875-6". CMP has widths of 48", 60", and 72" with a thickness ranging between 0.1875-0.500". Steel plate can also be classified as Heavy Steel Plate, and this accounts for any material that has a thickness greater than 3". Be sure to check out our product pages "Steel Sheet" and "Hot Rolled Plate" to find out the specific products we have to offer!

